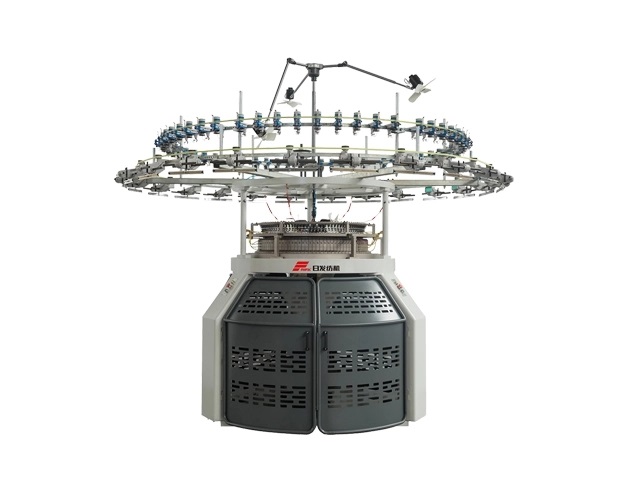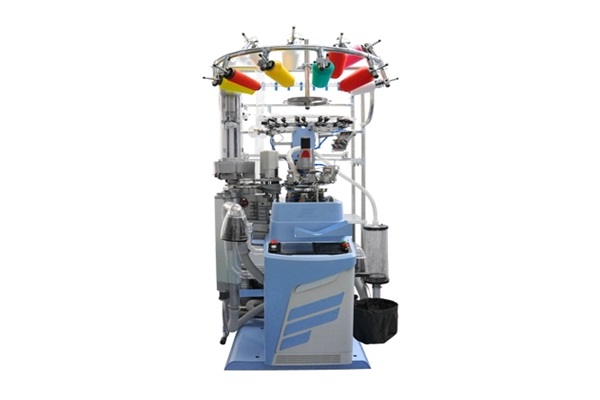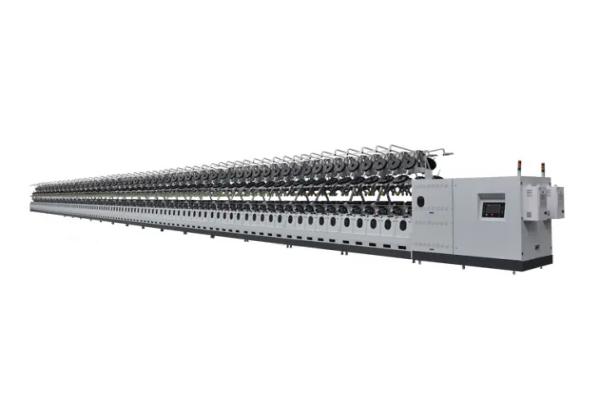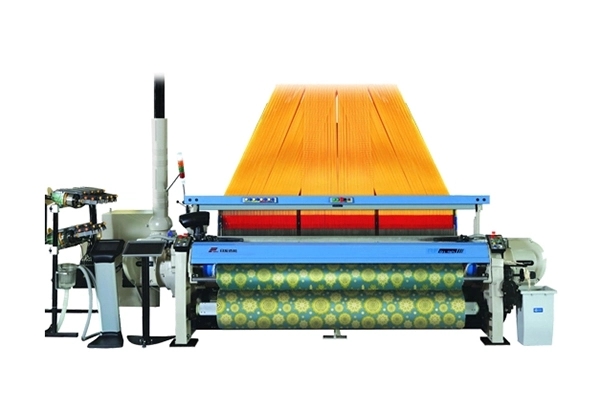

- Doubling
- Staple Fiber Yarns
- Texturing
- Normal Filament Fiber Yarns
- Carpet Yarns
- Tire Cord Yarns
-
RFAW20
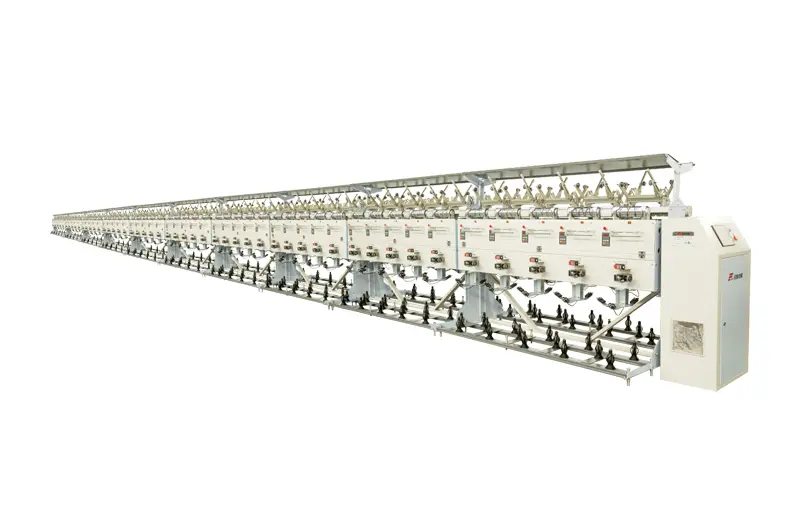 This new assembly winder machine, featuring a grooved drum, is an optimized version of the original model with an improved yarn guiding path. It is capable of combining 2 to 3 strands of cotton, hemp, wool, and certain blended yarns into a doubling bobbin. This makes it suitable for subsequent processing stages, such as using a two-for-one twister machine.
This new assembly winder machine, featuring a grooved drum, is an optimized version of the original model with an improved yarn guiding path. It is capable of combining 2 to 3 strands of cotton, hemp, wool, and certain blended yarns into a doubling bobbin. This makes it suitable for subsequent processing stages, such as using a two-for-one twister machine. -
RFAW22
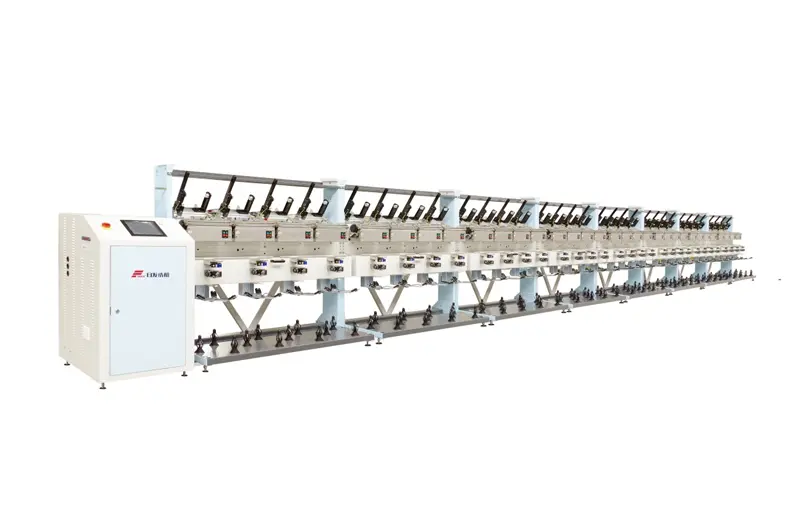 Drawing on advanced technologies from both domestic and international sources, our company has designed and developed a new type of precision assembly winder machine that leads the industry in technical sophistication. Through precise calculation and arrangement of the yarn track, the winding density can be increased by at least 30% without increasing tension. The machine operates using a single spindle control mode, with all functions managed and operated on the control terminal, enabling real-time monitoring.
Drawing on advanced technologies from both domestic and international sources, our company has designed and developed a new type of precision assembly winder machine that leads the industry in technical sophistication. Through precise calculation and arrangement of the yarn track, the winding density can be increased by at least 30% without increasing tension. The machine operates using a single spindle control mode, with all functions managed and operated on the control terminal, enabling real-time monitoring.
-
RFTS20D
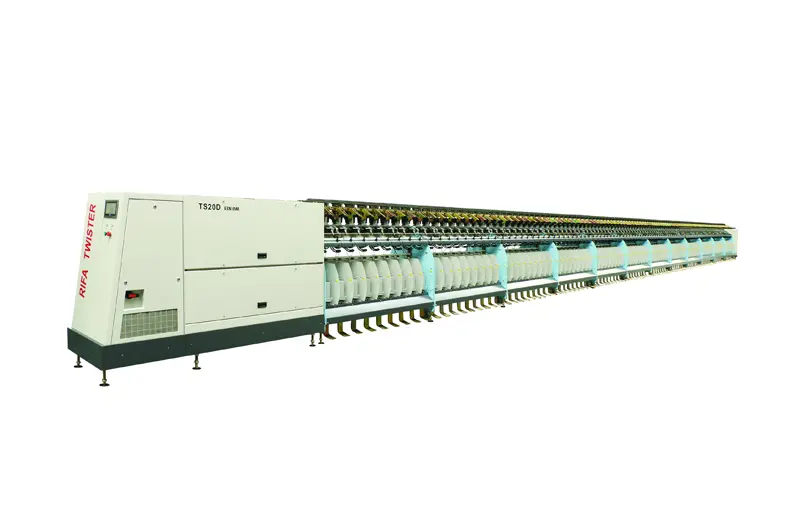 The RFTS20D short fiber twister is a versatile machine primarily designed for twisting strand threads in various fields such as cotton spinning, sewing thread production, core spun yarn, wool spinning, and blending. Its wide range of applications makes it a valuable asset in any textile production setting. The equipment is designed with a modular approach, allowing for flexible configuration of various functional modules to meet different production needs.
The RFTS20D short fiber twister is a versatile machine primarily designed for twisting strand threads in various fields such as cotton spinning, sewing thread production, core spun yarn, wool spinning, and blending. Its wide range of applications makes it a valuable asset in any textile production setting. The equipment is designed with a modular approach, allowing for flexible configuration of various functional modules to meet different production needs. -
RFTF20D
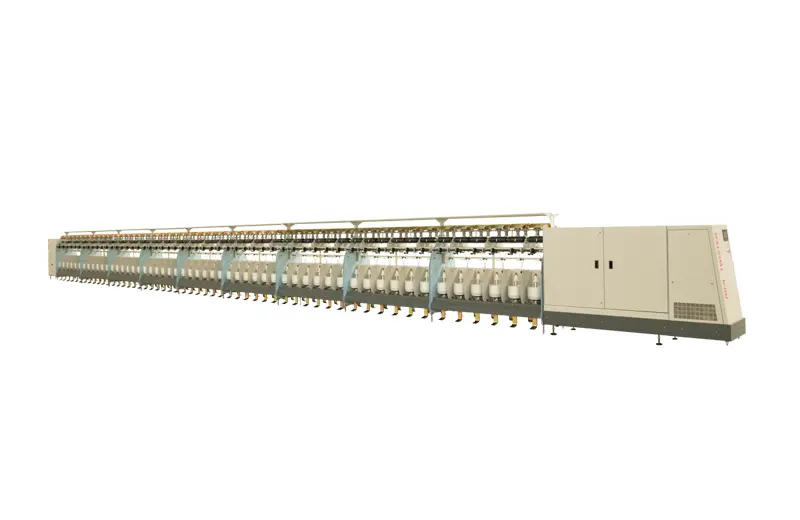 The product is a medium-package twister machine developed by our company. It is designed to handle single or multi-strand twisting of various filament fibers such as POY, HDY, FDY, DTY, and more. It is also suitable for processing a variety of carpet yarns, lawn yarns, and various staple coarse yarns. This versatile machine is a valuable addition to any textile production operation.
The product is a medium-package twister machine developed by our company. It is designed to handle single or multi-strand twisting of various filament fibers such as POY, HDY, FDY, DTY, and more. It is also suitable for processing a variety of carpet yarns, lawn yarns, and various staple coarse yarns. This versatile machine is a valuable addition to any textile production operation. -
RFTS30D
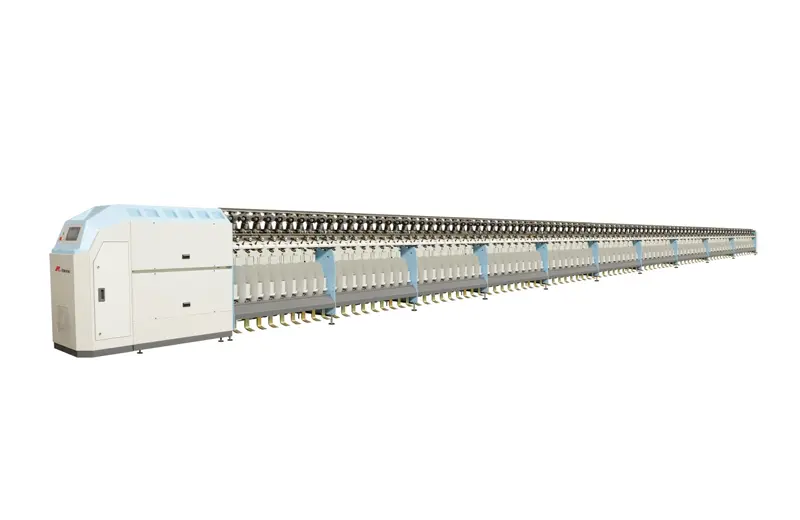 Building on the existing RFTS20D short fiber twister machine, we have developed a new and improved pneumatic two-for-one twister machine. This optimized version offers enhanced performance and efficiency, providing a superior solution for textile production needs.
Building on the existing RFTS20D short fiber twister machine, we have developed a new and improved pneumatic two-for-one twister machine. This optimized version offers enhanced performance and efficiency, providing a superior solution for textile production needs.
-
RFFT10
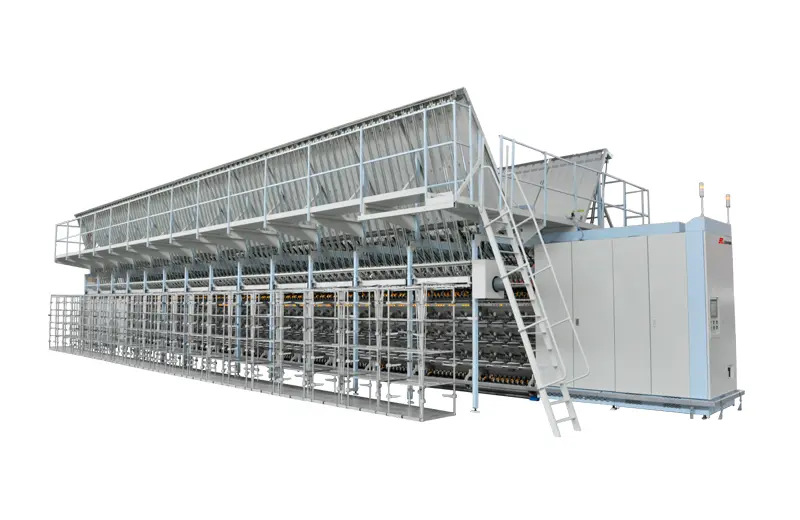 This machine primarily processes POY yarn (Pre-oriented Yarn) through stretching and false twisting deformation, transforming it into low elastic or high elastic false twisting texturing yarn (DTY). If equipped with an optional interlaced nozzle, the machine can also produce intermingle yarn. This makes it a versatile and valuable tool for any textile production operation.
This machine primarily processes POY yarn (Pre-oriented Yarn) through stretching and false twisting deformation, transforming it into low elastic or high elastic false twisting texturing yarn (DTY). If equipped with an optional interlaced nozzle, the machine can also produce intermingle yarn. This makes it a versatile and valuable tool for any textile production operation.
-
RF310
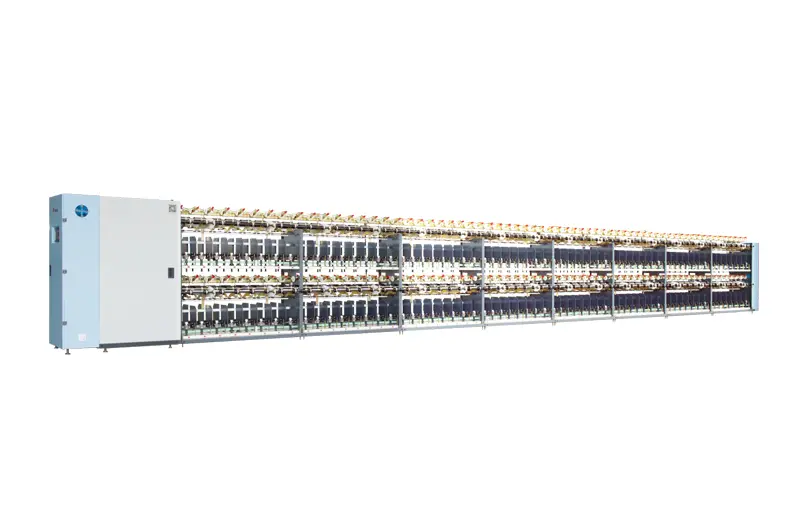 Since the introduction of our twister in 1993, we have sold over 3.5 million spindles. Our strict quality requirements have ensured that our RIFA twister is recognized for its "high stability", "high efficiency", and "high quality". This commitment to excellence has earned us high praise from our users.
Since the introduction of our twister in 1993, we have sold over 3.5 million spindles. Our strict quality requirements have ensured that our RIFA twister is recognized for its "high stability", "high efficiency", and "high quality". This commitment to excellence has earned us high praise from our users. -
RFTI11
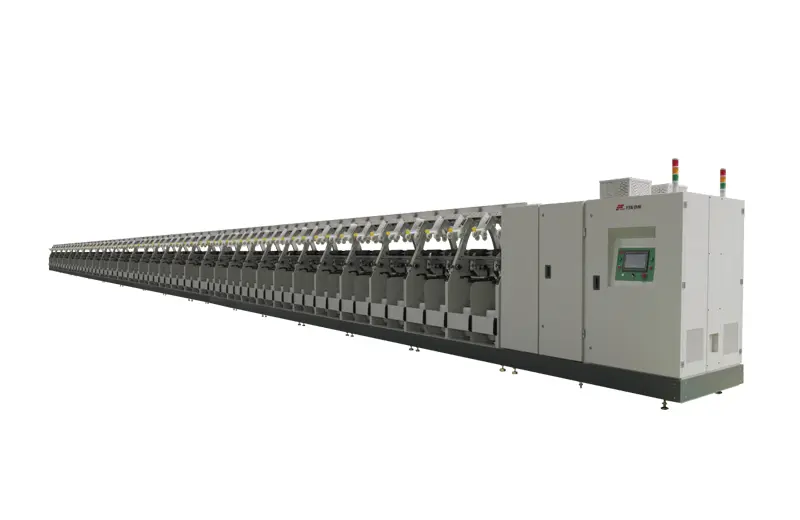 The TI11 electric spindle two-for-one twister machine is a state-of-the-art piece of equipment in which the spindle is directly driven by the motor, ensuring stable spindle speed. This model is designed to achieve the goal of single spindle control, allowing for real-time monitoring of related data from a single spindle. This feature enhances the precision and efficiency of the machine, making it a valuable asset for any textile production operation.
The TI11 electric spindle two-for-one twister machine is a state-of-the-art piece of equipment in which the spindle is directly driven by the motor, ensuring stable spindle speed. This model is designed to achieve the goal of single spindle control, allowing for real-time monitoring of related data from a single spindle. This feature enhances the precision and efficiency of the machine, making it a valuable asset for any textile production operation.
-
RFCC11
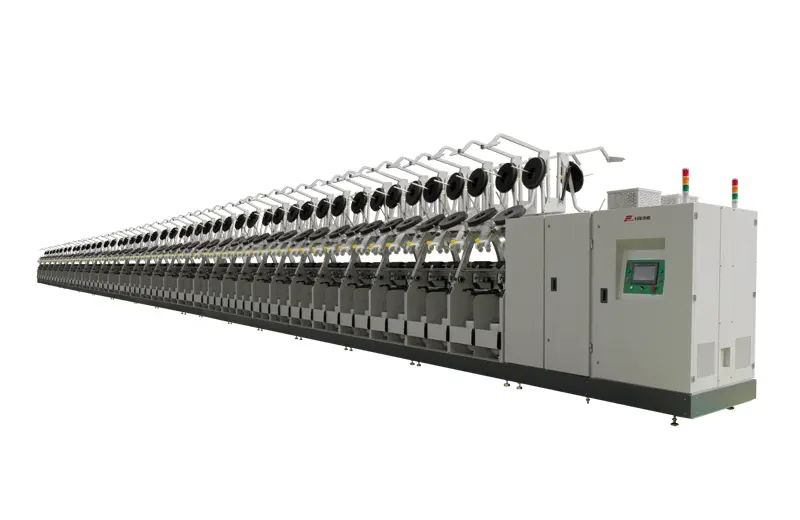 The CC11 is a new type of direct twisting machine that our company has developed specifically for yarn used in the carpet industry. This innovative machine uses a one-time merging method with a single processing step, significantly reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. As a result, the yarn capacity is higher compared to the two-for-one twister machine, and it operates with less power consumption.
The CC11 is a new type of direct twisting machine that our company has developed specifically for yarn used in the carpet industry. This innovative machine uses a one-time merging method with a single processing step, significantly reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. As a result, the yarn capacity is higher compared to the two-for-one twister machine, and it operates with less power consumption.
-
RFTC21A
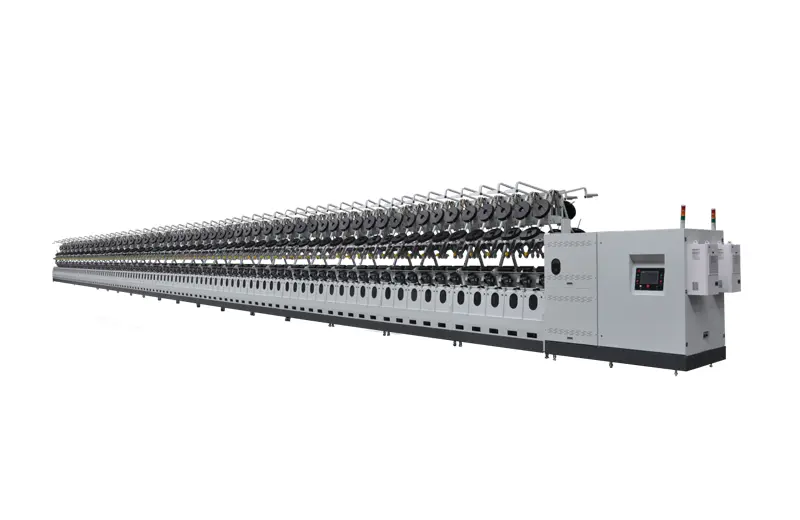 The Direct Twisting Machine for Tire Cord, designed and developed by our company, is a revolutionary piece of equipment that merges processes into a single step, reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. This not only increases the yarn capacity compared to the two-for-one twister machine but also enhances production efficiency, reduces labor, and reduces on energy consumption.
The Direct Twisting Machine for Tire Cord, designed and developed by our company, is a revolutionary piece of equipment that merges processes into a single step, reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. This not only increases the yarn capacity compared to the two-for-one twister machine but also enhances production efficiency, reduces labor, and reduces on energy consumption. -
RFTC21B
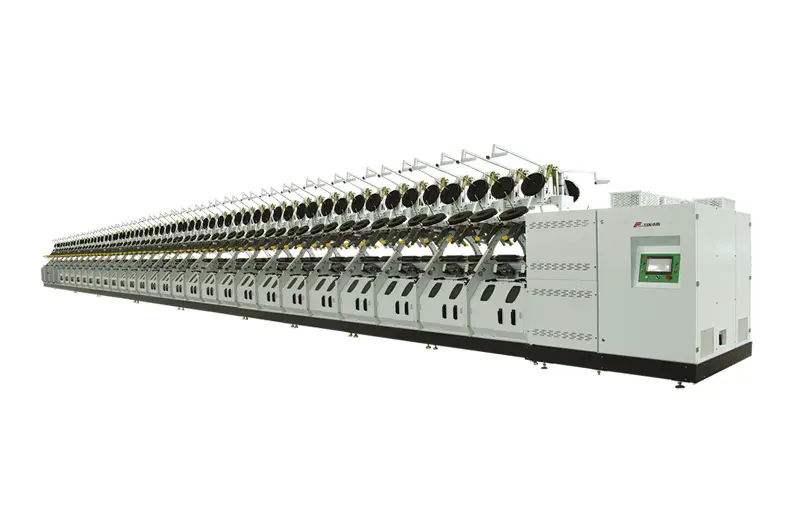 Our Direct Twisting Machine for Tire Cord is a game-changer in the textile industry. It uses a single processing method that merges all steps into one, significantly reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. This results in a higher yarn capacity compared to the two-for-one twister machine.
Our Direct Twisting Machine for Tire Cord is a game-changer in the textile industry. It uses a single processing method that merges all steps into one, significantly reducing the number of stages compared to traditional twisting methods. This results in a higher yarn capacity compared to the two-for-one twister machine.
- Pre Spinning
- Spinning
-
Blowroom
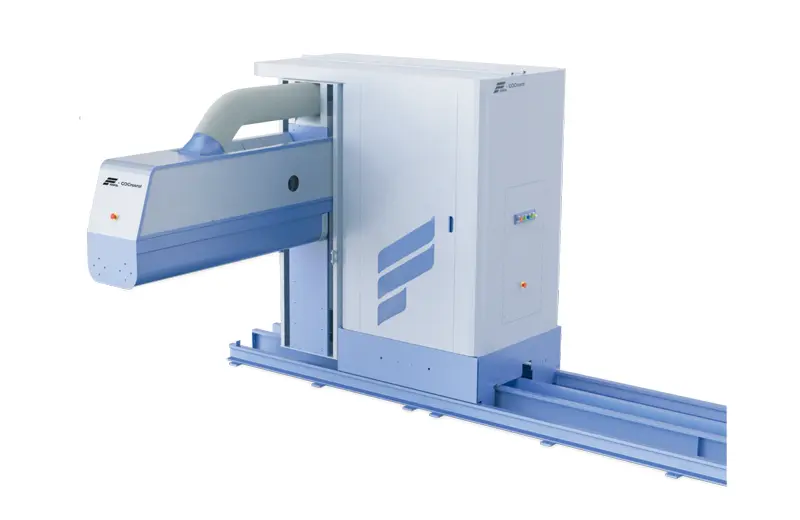 Blow-room machinery is used in the textile industry for the initial processing of raw fibers. It cleans, opens, and blends fibers, preparing them for further processing in textile production.
Blow-room machinery is used in the textile industry for the initial processing of raw fibers. It cleans, opens, and blends fibers, preparing them for further processing in textile production. -
MK8
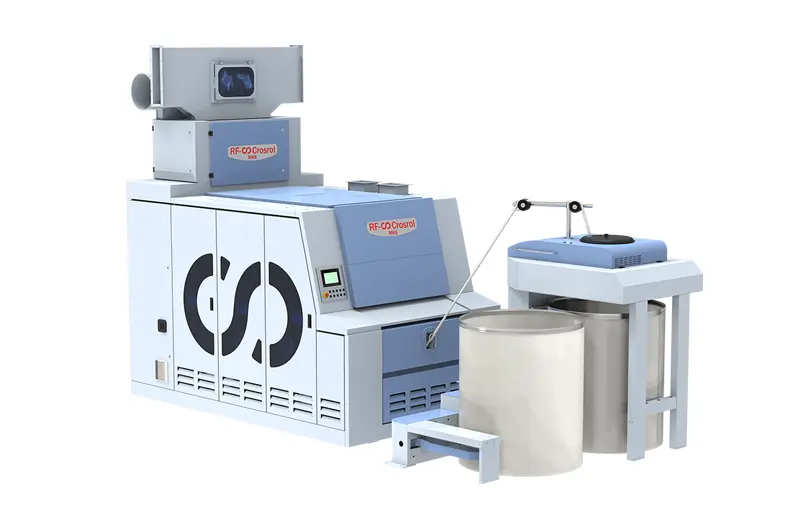 Rifa's pre-spinning technology evolved from the original technology of Crosrol in the United Kingdom. Leveraging the robust technological research and development platform of Rifa Textile Machinery, we have continuously innovated and bravely pushed boundaries to develop full-process pre-spinning equipment with core competitiveness. Rifa is dedicated to providing customers with superior intelligent solutions.
Rifa's pre-spinning technology evolved from the original technology of Crosrol in the United Kingdom. Leveraging the robust technological research and development platform of Rifa Textile Machinery, we have continuously innovated and bravely pushed boundaries to develop full-process pre-spinning equipment with core competitiveness. Rifa is dedicated to providing customers with superior intelligent solutions. -
RFCA10
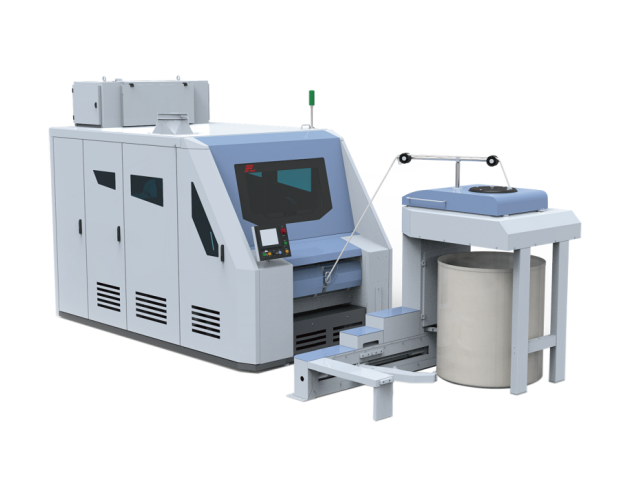 The RFCA10 carding machine is a new generation of high production carding machine independently developed by Anhui Rifa Textile Machinery Co.,Ltd. It has increased carding area, reduced floor space, s...
The RFCA10 carding machine is a new generation of high production carding machine independently developed by Anhui Rifa Textile Machinery Co.,Ltd. It has increased carding area, reduced floor space, s... -
RFDF12
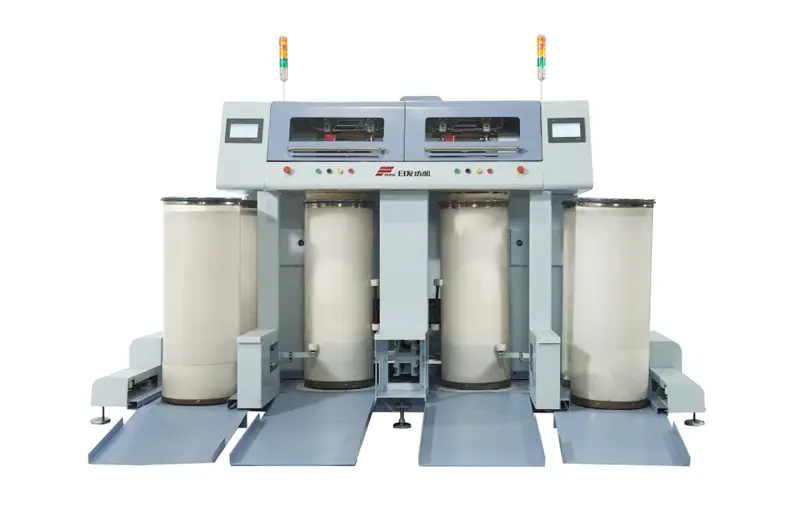 The RFDF12 is a high-speed drawing frame with a two-delivery autoleveller. This machine is built with a high-precision and high-strength casting structure. It utilizes an internationally recognized industrial control computer, a true color human-machine interface, a high-response servo system, and an intelligent detection sensor that eliminates any 'blind side'.
The RFDF12 is a high-speed drawing frame with a two-delivery autoleveller. This machine is built with a high-precision and high-strength casting structure. It utilizes an internationally recognized industrial control computer, a true color human-machine interface, a high-response servo system, and an intelligent detection sensor that eliminates any 'blind side'.
-
RFVS10
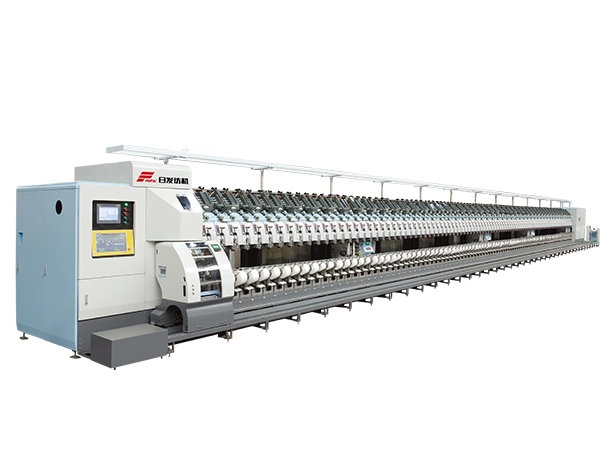 The core technical indicators of Rifa VS10 fully automatic air jet vortex spinning machine have reached the level of imported equipment.Reasonable spinning function layoutComprehensive control of yarn...
The core technical indicators of Rifa VS10 fully automatic air jet vortex spinning machine have reached the level of imported equipment.Reasonable spinning function layoutComprehensive control of yarn... -
RFRS30D
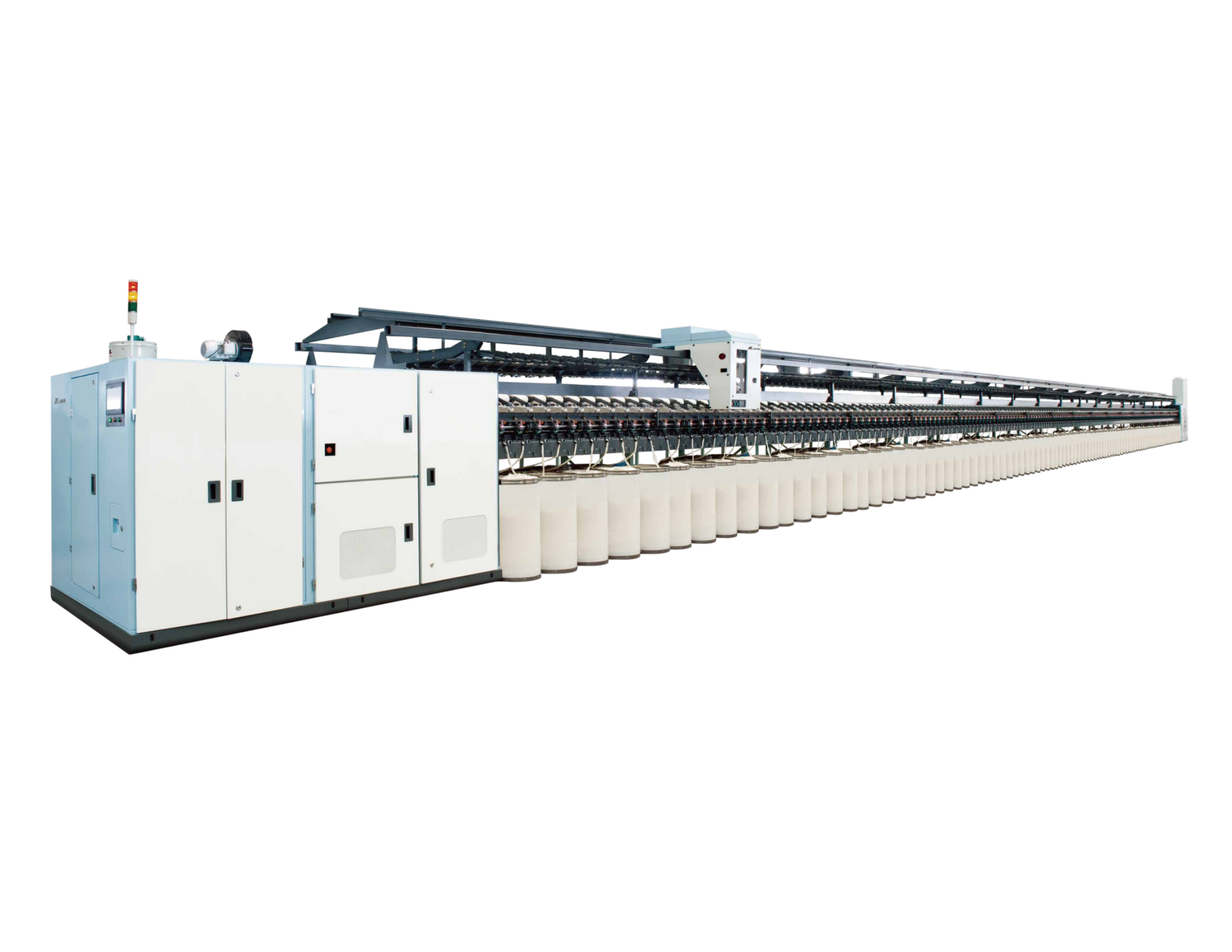 Max spindles is up to 600 spindles, and the highest rotor design speed of 110,000RPM.Modular design and abundant optional accessories to meet the needs of different customers.Innovative auto doffing ...
Max spindles is up to 600 spindles, and the highest rotor design speed of 110,000RPM.Modular design and abundant optional accessories to meet the needs of different customers.Innovative auto doffing ... -
RFRS51
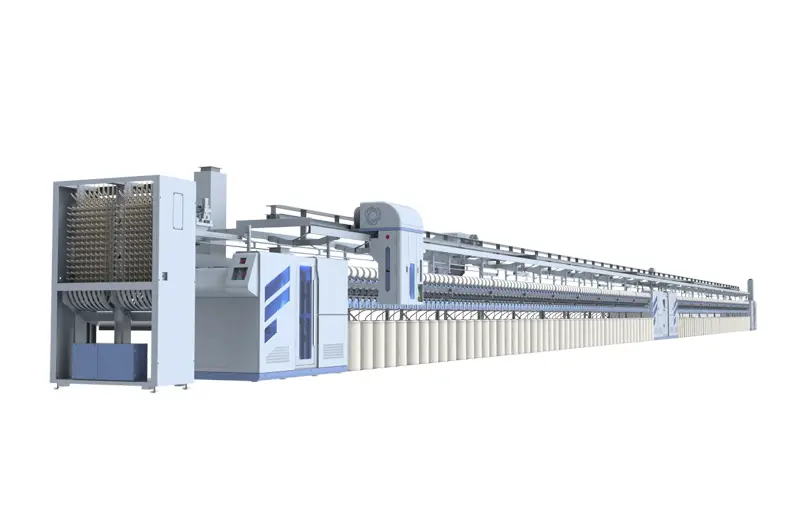 The RS51 rotor spinning machine, featuring single spindle yarn take-up technology, is a product that combines simplicity of operation with advanced automation. It is characterized by a high number of rotors, high speed, versatility, and high efficiency.
The RS51 rotor spinning machine, featuring single spindle yarn take-up technology, is a product that combines simplicity of operation with advanced automation. It is characterized by a high number of rotors, high speed, versatility, and high efficiency.
- Air Jet Looms
- Rapier Looms
- Water Jet Looms
- Terry Looms
- Automatic Drawing-in Machines
-
RFJA30
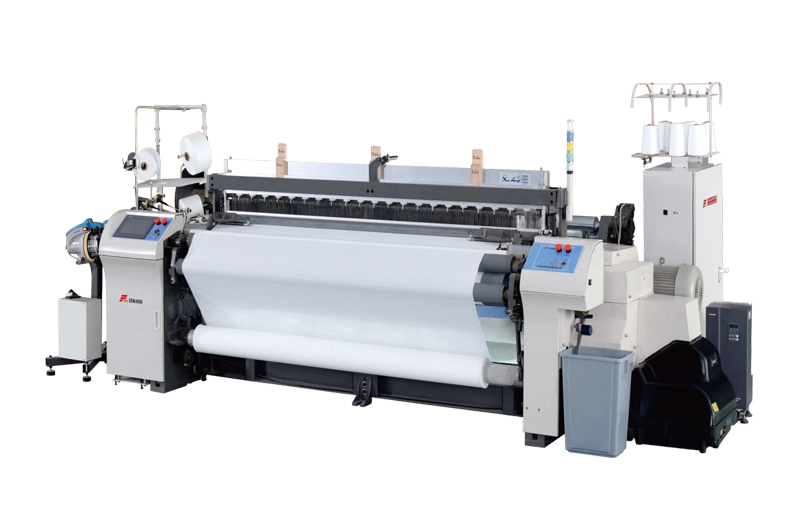 RFJA30 air jet loom is developed by our company which has advanced performance on the base of the merit of RFJA20 it is developed for meeting higher weaving requirement. This loom offers superior perf...
RFJA30 air jet loom is developed by our company which has advanced performance on the base of the merit of RFJA20 it is developed for meeting higher weaving requirement. This loom offers superior perf... -
RFJA30 Max
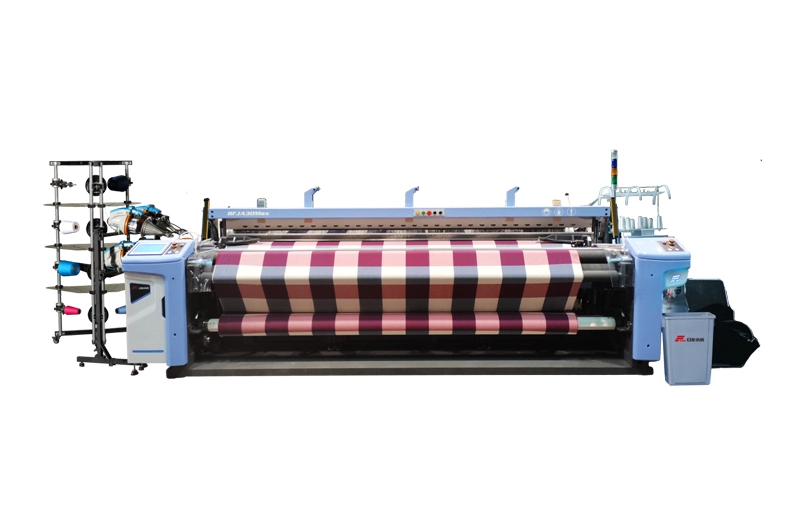 RFJA30Max air jet loom has advanced performance on the base of the merit of RFJA30, it is developed for meeting higher weaving requirement. This loom offers superior performance, incorporating the lat...
RFJA30Max air jet loom has advanced performance on the base of the merit of RFJA30, it is developed for meeting higher weaving requirement. This loom offers superior performance, incorporating the lat... -
RFJA32
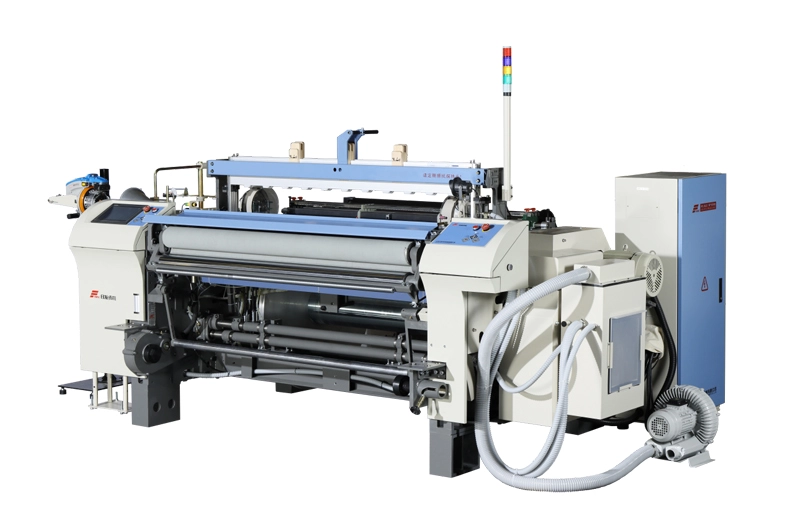 The RFJA32 Fiberglass Air Jet Loom is a specialized weaving machine designed for the production of glass fiber fabrics. The RFJA32 fiberglass weaving machine is specifically designed to handle the uni...
The RFJA32 Fiberglass Air Jet Loom is a specialized weaving machine designed for the production of glass fiber fabrics. The RFJA32 fiberglass weaving machine is specifically designed to handle the uni...
-
RFRL31
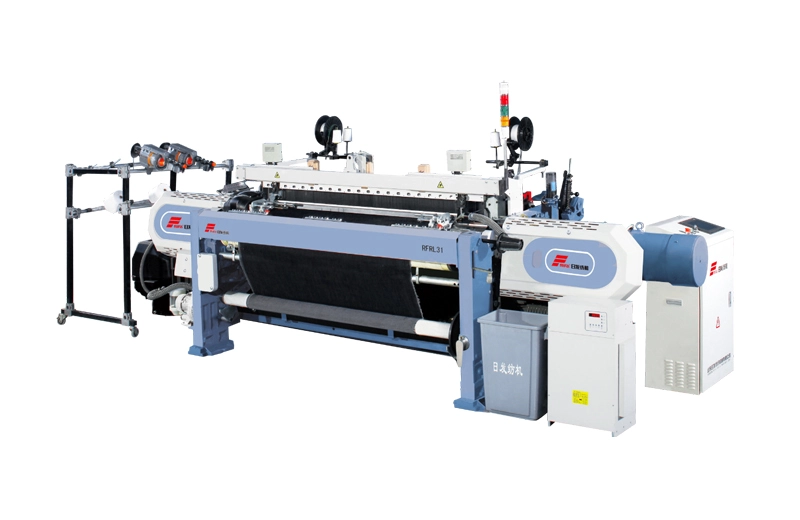 Shandong Rifa Textile Machinery Co., Ltd. always devotes herself to value-added study for textile technology, helping customers to get better production with economic cost. It is the basic of RFRL31 p...
Shandong Rifa Textile Machinery Co., Ltd. always devotes herself to value-added study for textile technology, helping customers to get better production with economic cost. It is the basic of RFRL31 p... -
RFRL50
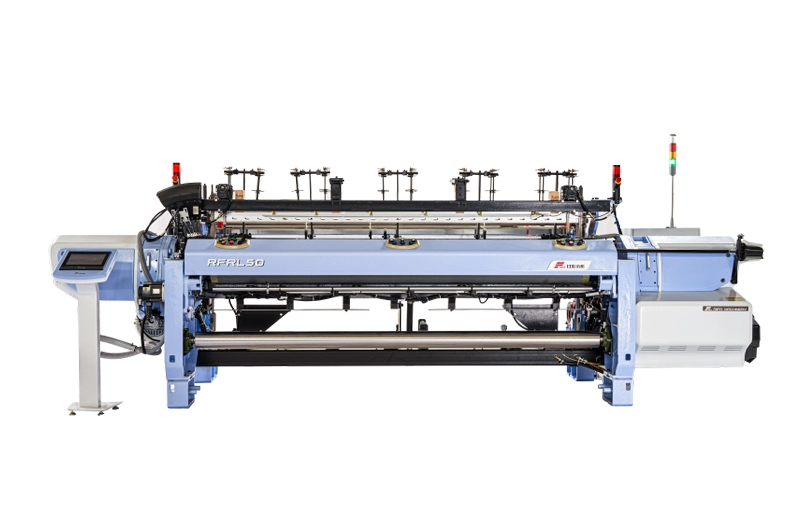 RFRL50 High Grade Rapier Loom is based on the research of textile technology value-added, which enables customers to produce better products more economically, and has the advanced functions of the in...
RFRL50 High Grade Rapier Loom is based on the research of textile technology value-added, which enables customers to produce better products more economically, and has the advanced functions of the in... -
RFRL90
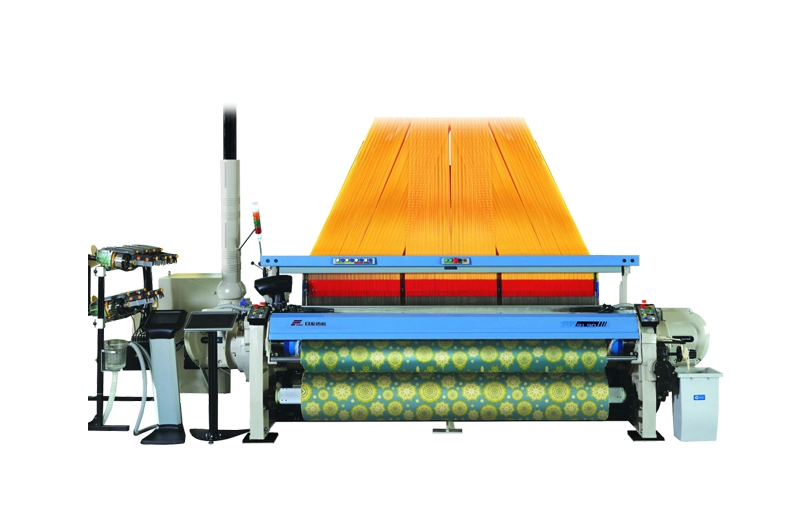 RFRL90 High Speed Rapier Loom is a newly designed loom based on our RFTL80 High End Rapier Towel Loom. It is designed to provide the market with a loom that combines quality, versatility, efficiency a...
RFRL90 High Speed Rapier Loom is a newly designed loom based on our RFTL80 High End Rapier Towel Loom. It is designed to provide the market with a loom that combines quality, versatility, efficiency a...
-
RFJW03
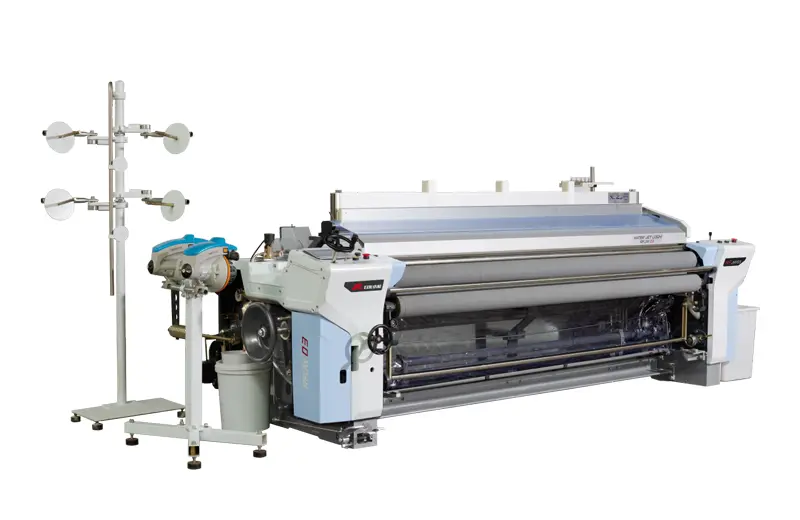 RFJW03 series water jet loom is suitable for weaving light and medium-thickness fabrics. Drawing on Rifa's experience in development of other water jet looms, the design is optimized, the weaving ...
RFJW03 series water jet loom is suitable for weaving light and medium-thickness fabrics. Drawing on Rifa's experience in development of other water jet looms, the design is optimized, the weaving ... -
RFJW05
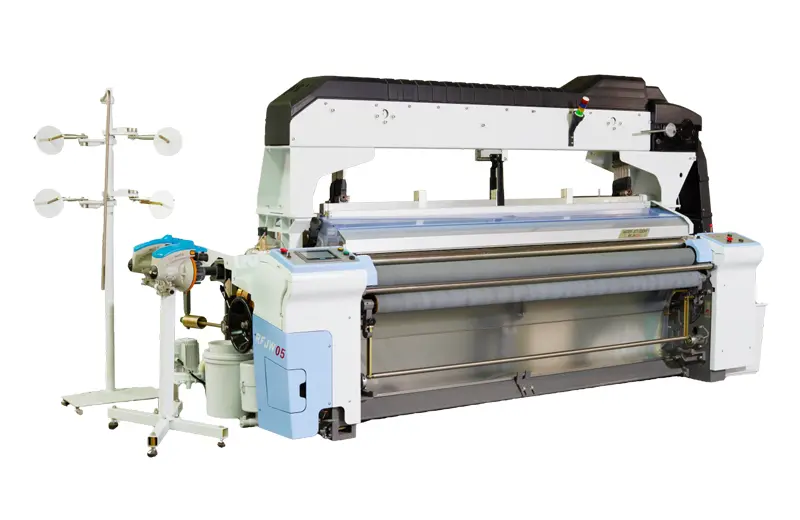 The RFJW05 series water jet looms are mid-range weaving machines that incorporate the advanced technology of shuttleless looms, such as Rifa air jet looms. Developed with a design concept focused on e...
The RFJW05 series water jet looms are mid-range weaving machines that incorporate the advanced technology of shuttleless looms, such as Rifa air jet looms. Developed with a design concept focused on e... -
RFJW10
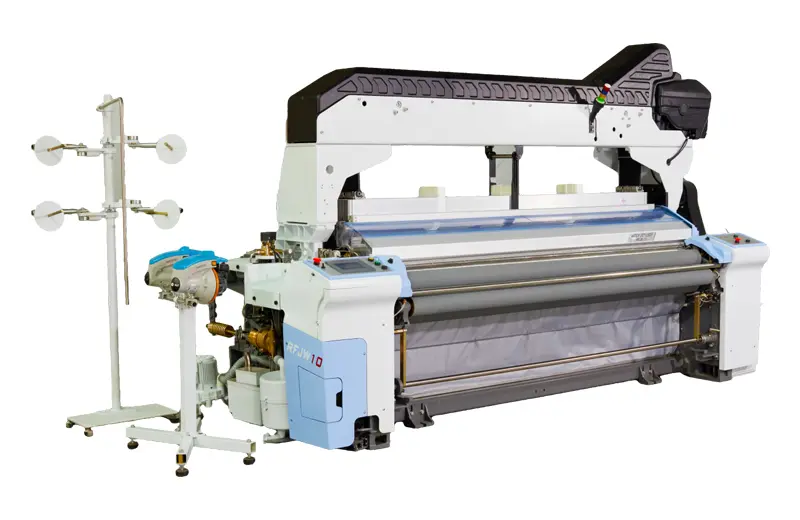 The RFJW series Water Jet looms are a testament to our commitment to innovation and technological advancement. Building on the technology of the RFJA air jet looms, these models are designed with the ...
The RFJW series Water Jet looms are a testament to our commitment to innovation and technological advancement. Building on the technology of the RFJA air jet looms, these models are designed with the ...
-
RFJAT28
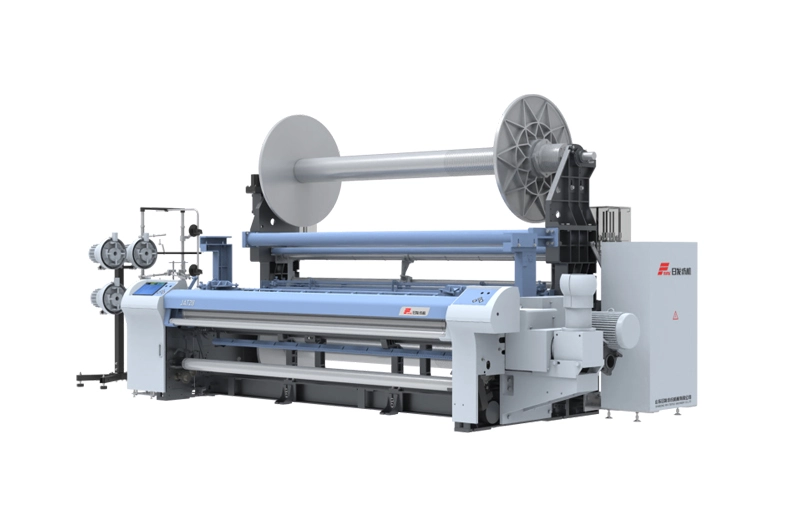 The RFJAT28 Air Jet Terry Loom is a specialized weaving machine designed for the production of terry cloth, a type of fabric with uncut loops that can absorb large amounts of waterThe RFJAT28 weaving ...
The RFJAT28 Air Jet Terry Loom is a specialized weaving machine designed for the production of terry cloth, a type of fabric with uncut loops that can absorb large amounts of waterThe RFJAT28 weaving ... -
RFJA33
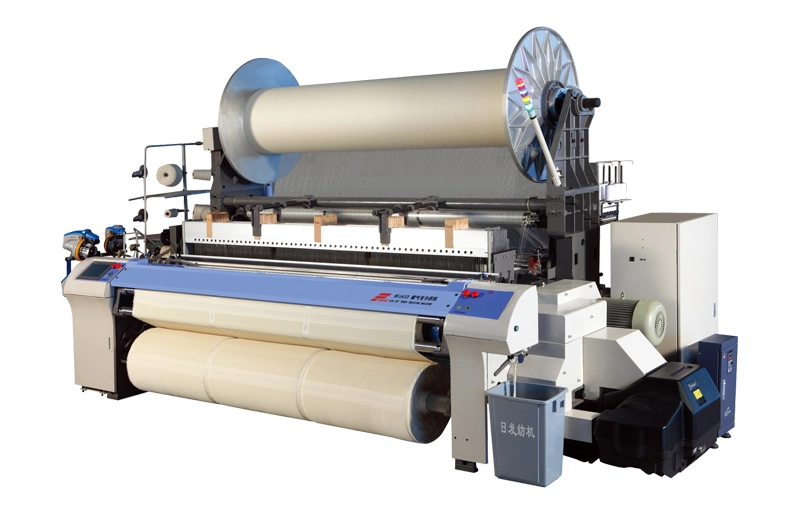 RFJA series air jet terry looms succeed the technology of RFJA series air jet looms, is a model of high speed air jet terry looms with the design concept of high speed, lower consumption and wide weav...
RFJA series air jet terry looms succeed the technology of RFJA series air jet looms, is a model of high speed air jet terry looms with the design concept of high speed, lower consumption and wide weav... -
RFTL80
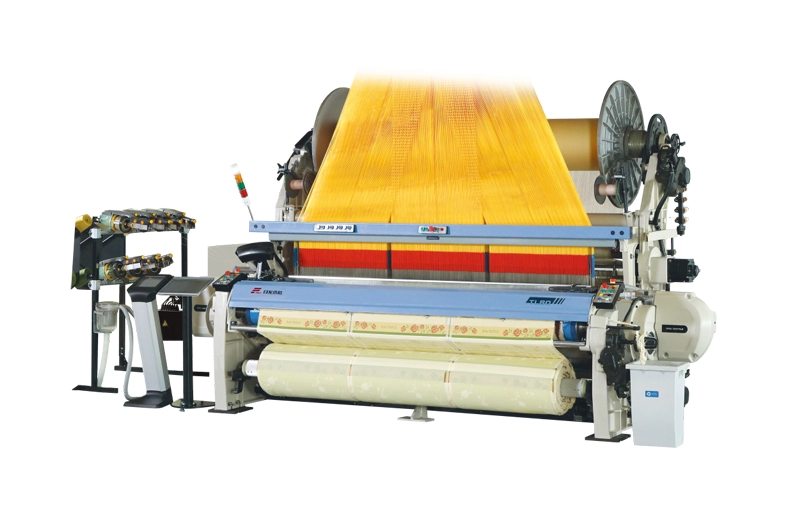 The RFTL80 Rapier Towel Loom is a newly designed towel loom. The aim is to offer the market a kind of weaving machine that combines the best in quality, versatility, efficiency and availability.
The RFTL80 Rapier Towel Loom is a newly designed towel loom. The aim is to offer the market a kind of weaving machine that combines the best in quality, versatility, efficiency and availability.
-
RFAD10
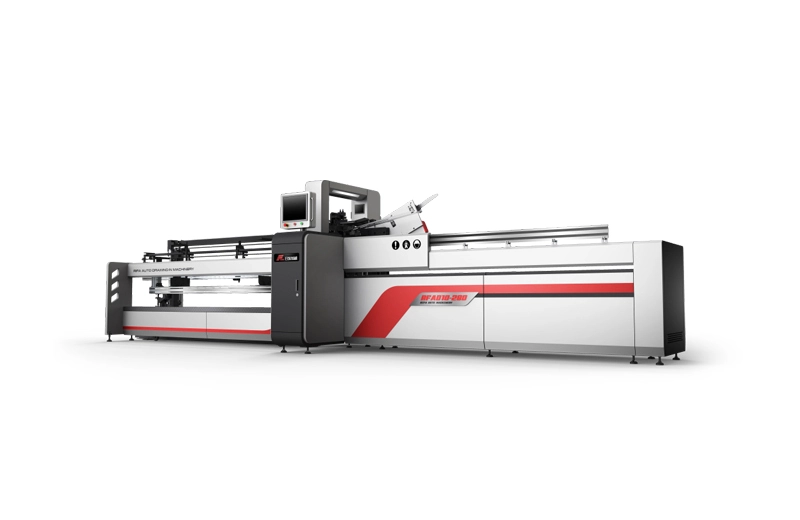 RFAD10 full-automatic drawing-in machine is a kind of drawing-in equipment based on seed yarn mode. Drawing-in is not related to the loom beam, so pre-drawing can be conducted in advance, pre-drawing ...
RFAD10 full-automatic drawing-in machine is a kind of drawing-in equipment based on seed yarn mode. Drawing-in is not related to the loom beam, so pre-drawing can be conducted in advance, pre-drawing ... -
RFAD20
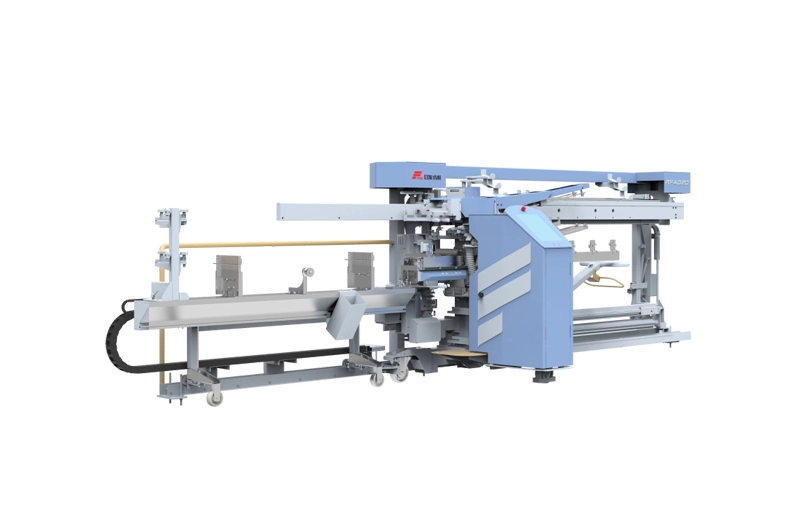 RFAD20 full-automatic drawing-in machine is equipment developed for meeting the demands for the drawing-in of chemical fiber filament yarn, the machine can be used for the drawing-in operation of suit...
RFAD20 full-automatic drawing-in machine is equipment developed for meeting the demands for the drawing-in of chemical fiber filament yarn, the machine can be used for the drawing-in operation of suit... -
RFAD30
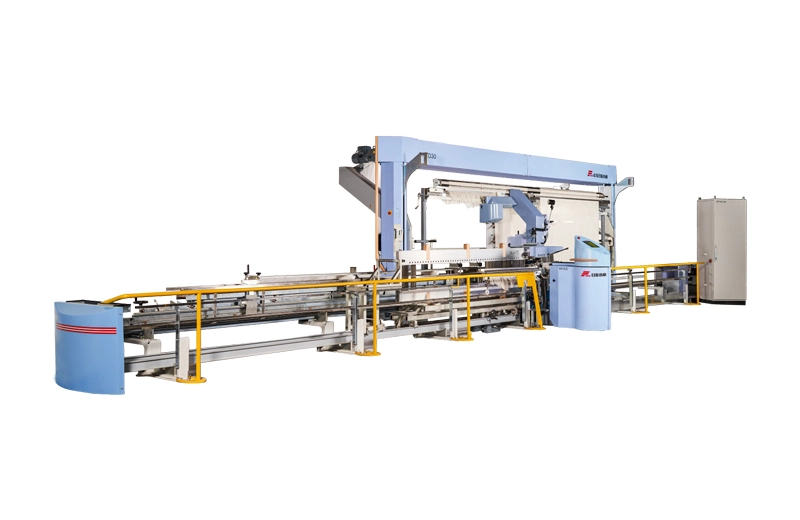 RFAD30 full-automatic drawing-in machine is a kind of equipment to deal with the drawing-in of the fabrics made with complex process.
RFAD30 full-automatic drawing-in machine is a kind of equipment to deal with the drawing-in of the fabrics made with complex process.
- Single Jersey
- Double Jersey
- Jacquard
- Seamless
- Socks
-
RFSK
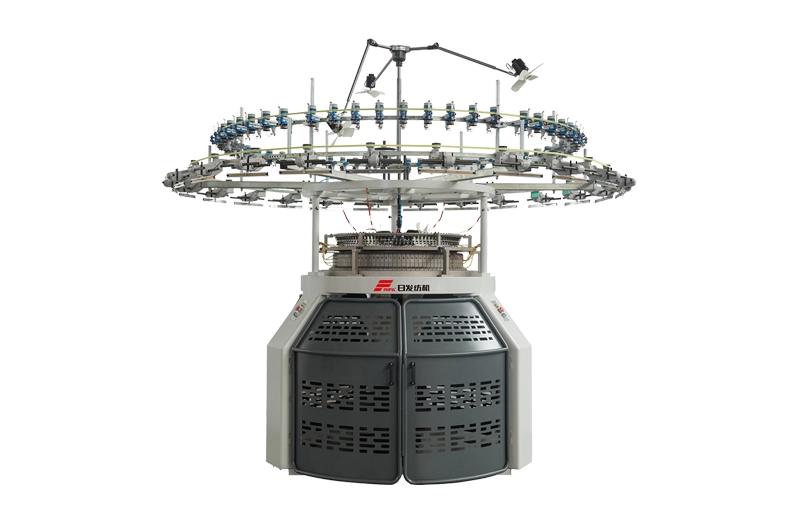 The RFSK high-speed single knitting machine series is a testament to RIFA's commitment to innovation and quality. These machines adopt a four-needle track design and are equipped with a new-type feeder, which improves the yarn feeding angle and tension, ensuring superior fabric quality.
The RFSK high-speed single knitting machine series is a testament to RIFA's commitment to innovation and quality. These machines adopt a four-needle track design and are equipped with a new-type feeder, which improves the yarn feeding angle and tension, ensuring superior fabric quality. -
RFSTF
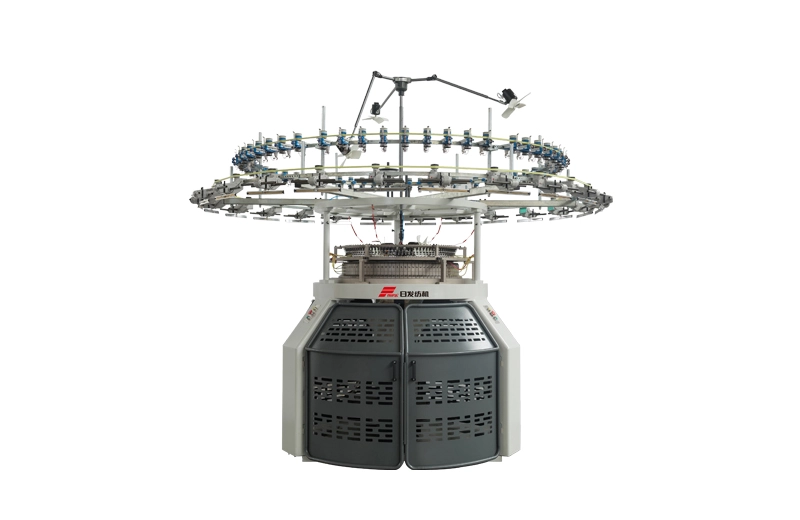 The RFSTF Three-thread Fleece Knitting Machine is a specialized knitting machine designed for producing sweaters. It features three lines for efficient and high-quality sweater production.
The RFSTF Three-thread Fleece Knitting Machine is a specialized knitting machine designed for producing sweaters. It features three lines for efficient and high-quality sweater production. -
RFSKP
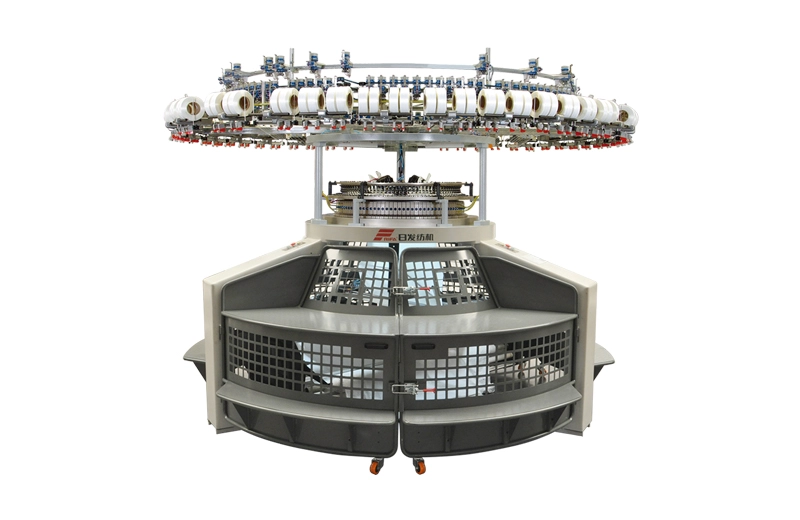 The RFSKP Single Open-Width Knitting Machine is an industrial device used for cutting or slitting materials like paper, film, foil, and metal into narrower rolls or sheets.
The RFSKP Single Open-Width Knitting Machine is an industrial device used for cutting or slitting materials like paper, film, foil, and metal into narrower rolls or sheets.
-
RFDK
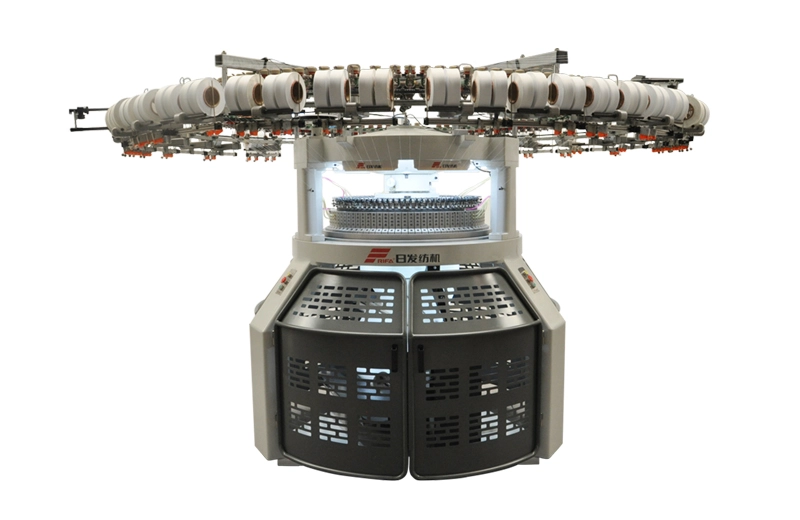 The RFDK Double Knitting Machine is a specialized device used for creating two layers of fabric simultaneously, allowing for reversible designs and increased warmth in the finished product.
The RFDK Double Knitting Machine is a specialized device used for creating two layers of fabric simultaneously, allowing for reversible designs and increased warmth in the finished product. -
RFDKP
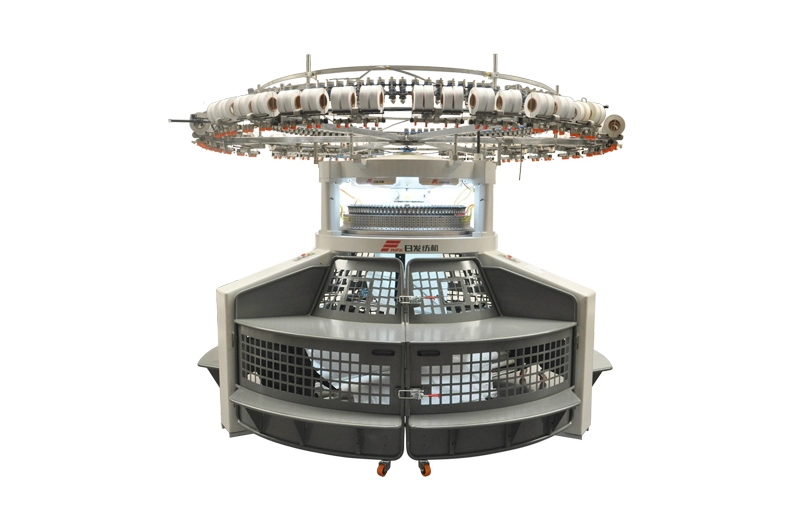 The RFDKP Double Open-Width Knitting Machine is an industrial device used for precision cutting of materials like paper, film, foil, and others into narrower rolls, enhancing efficiency in production processes.
The RFDKP Double Open-Width Knitting Machine is an industrial device used for precision cutting of materials like paper, film, foil, and others into narrower rolls, enhancing efficiency in production processes.
-
RFSJ
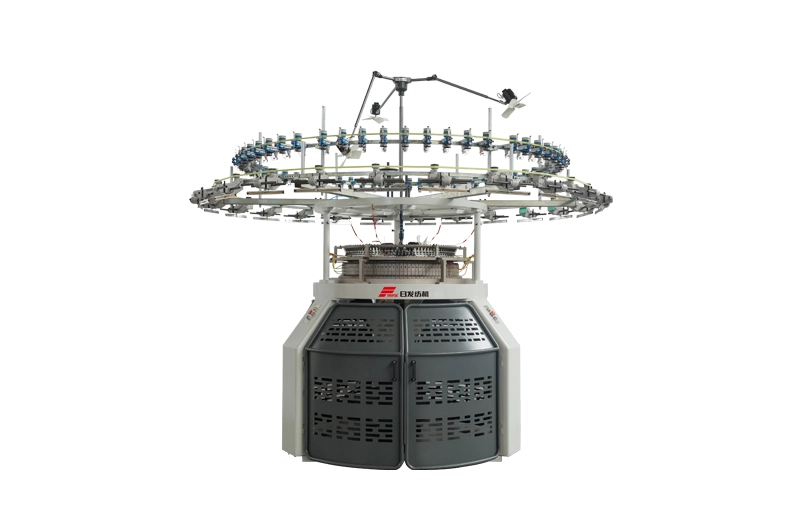 The RFSJ Single Computerized Jacquard Machine is a high-tech textile machine used for weaving intricate patterns and designs, controlled by computer programming for precision and efficiency.
The RFSJ Single Computerized Jacquard Machine is a high-tech textile machine used for weaving intricate patterns and designs, controlled by computer programming for precision and efficiency. -
RFDJ
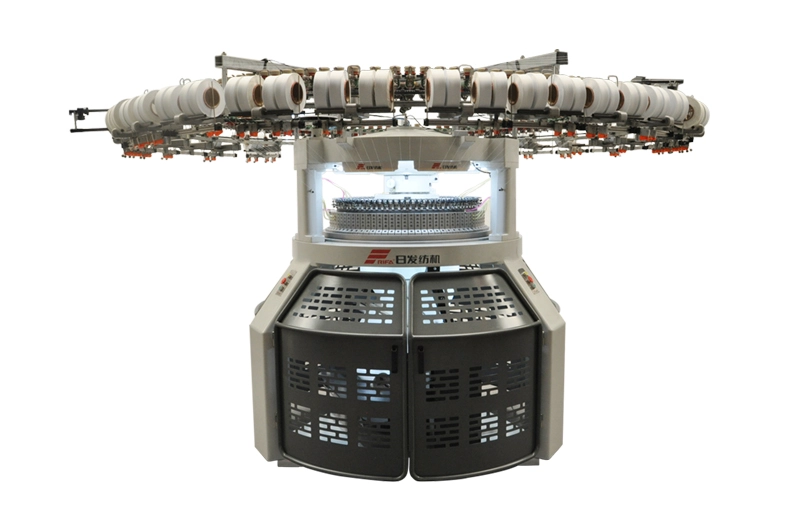 The RFDJ Double Computerized Jacquard Machine is an advanced textile machine used for creating intricate patterns and designs on fabrics, utilizing computerized technology for precision and efficiency.
The RFDJ Double Computerized Jacquard Machine is an advanced textile machine used for creating intricate patterns and designs on fabrics, utilizing computerized technology for precision and efficiency.
-
RFSM20
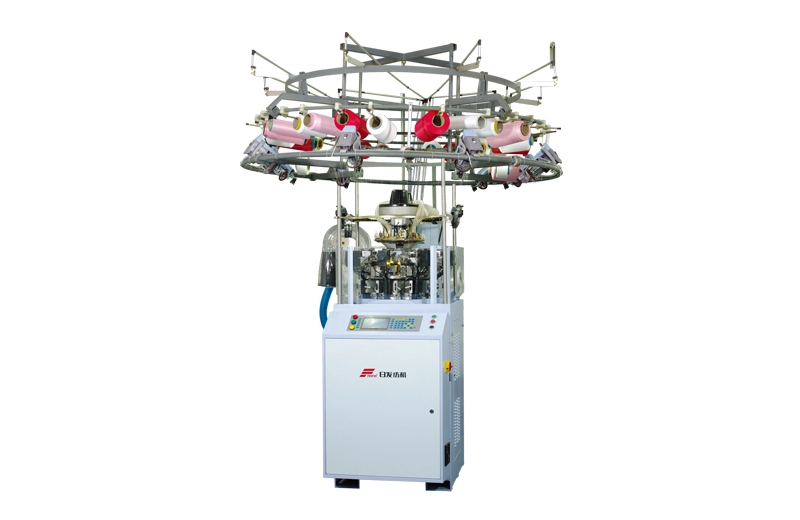 RIFA Textile Machinery is dedicated to the research and development of value-added knitting technology. Our goal is to assist our customers in producing superior products in a more cost-effective manner. A prime example of this commitment is the successful development of our RFSM series seamless machine.
RIFA Textile Machinery is dedicated to the research and development of value-added knitting technology. Our goal is to assist our customers in producing superior products in a more cost-effective manner. A prime example of this commitment is the successful development of our RFSM series seamless machine. -
RFSM30
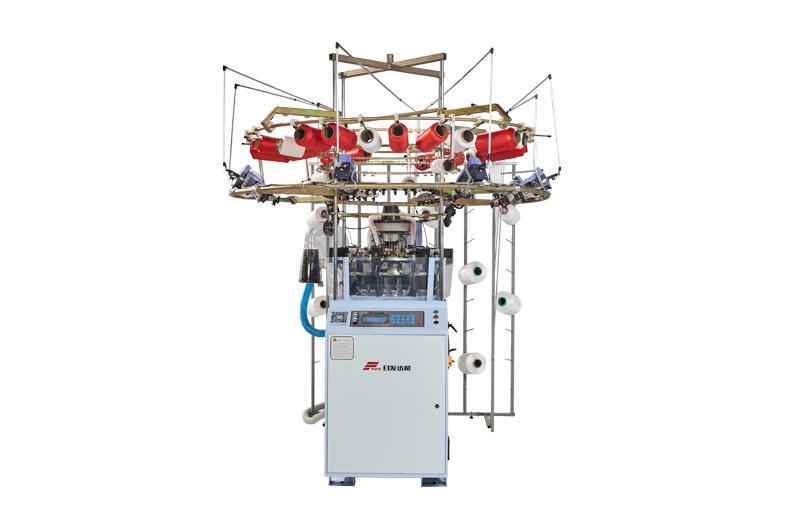 The RFSM30 High-Speed Seamless Machine is an advanced industrial machine designed for the rapid production of underwear, featuring high efficiency, precision, and quality in textile manufacturing.
The RFSM30 High-Speed Seamless Machine is an advanced industrial machine designed for the rapid production of underwear, featuring high efficiency, precision, and quality in textile manufacturing.
-
RFHM10
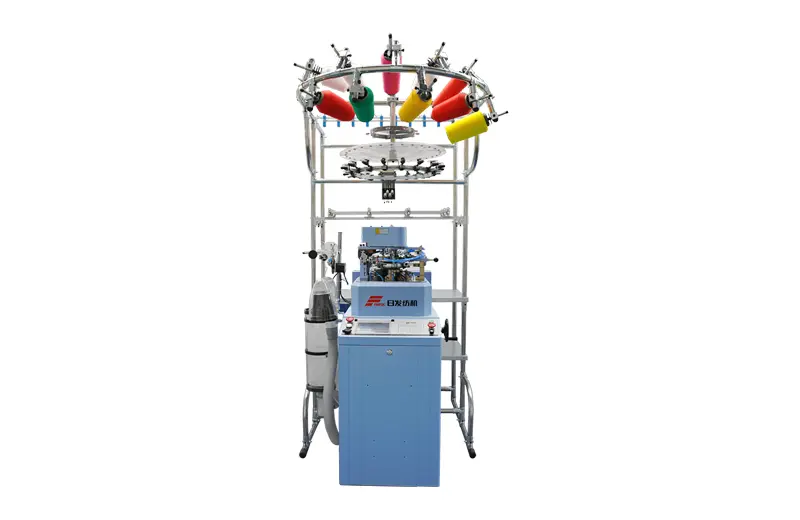 Our fully computerized hosiery machine (Regular model) is a versatile and efficient piece of equipment, designed to work with a wide range of raw materials. Whether you're using cotton yarn, nylon, polypropylene, polyester, or viscose, this machine can handle it all.
Our fully computerized hosiery machine (Regular model) is a versatile and efficient piece of equipment, designed to work with a wide range of raw materials. Whether you're using cotton yarn, nylon, polypropylene, polyester, or viscose, this machine can handle it all. -
RFHM20
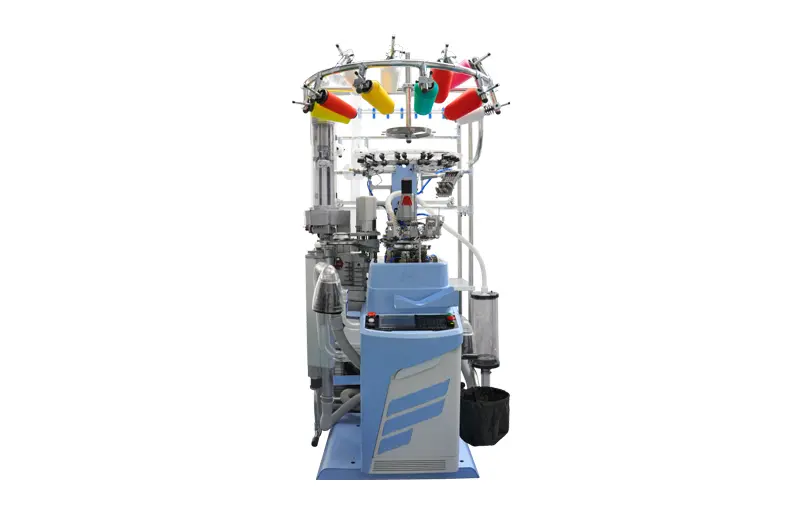 Our fully computerized single cylinder socks knitting machine is a state-of-the-art piece of equipment that integrates knitting, linking, and turning-out processes. It comes equipped with a stable stitch by stitch linking device, ensuring consistent and high-quality results.
Our fully computerized single cylinder socks knitting machine is a state-of-the-art piece of equipment that integrates knitting, linking, and turning-out processes. It comes equipped with a stable stitch by stitch linking device, ensuring consistent and high-quality results.
What are you looking for?
 English
English  français
français  Español
Español  русский
русский  português
português  Türkçe
Türkçe  العربية
العربية  한국어
한국어  فارسی
فارسی  Malay
Malay 



